This post is the third of a series of five articles written by Rice University undergraduate students who participated in the spring semester Kinder Houston Area Survey course. Read the first and second post.
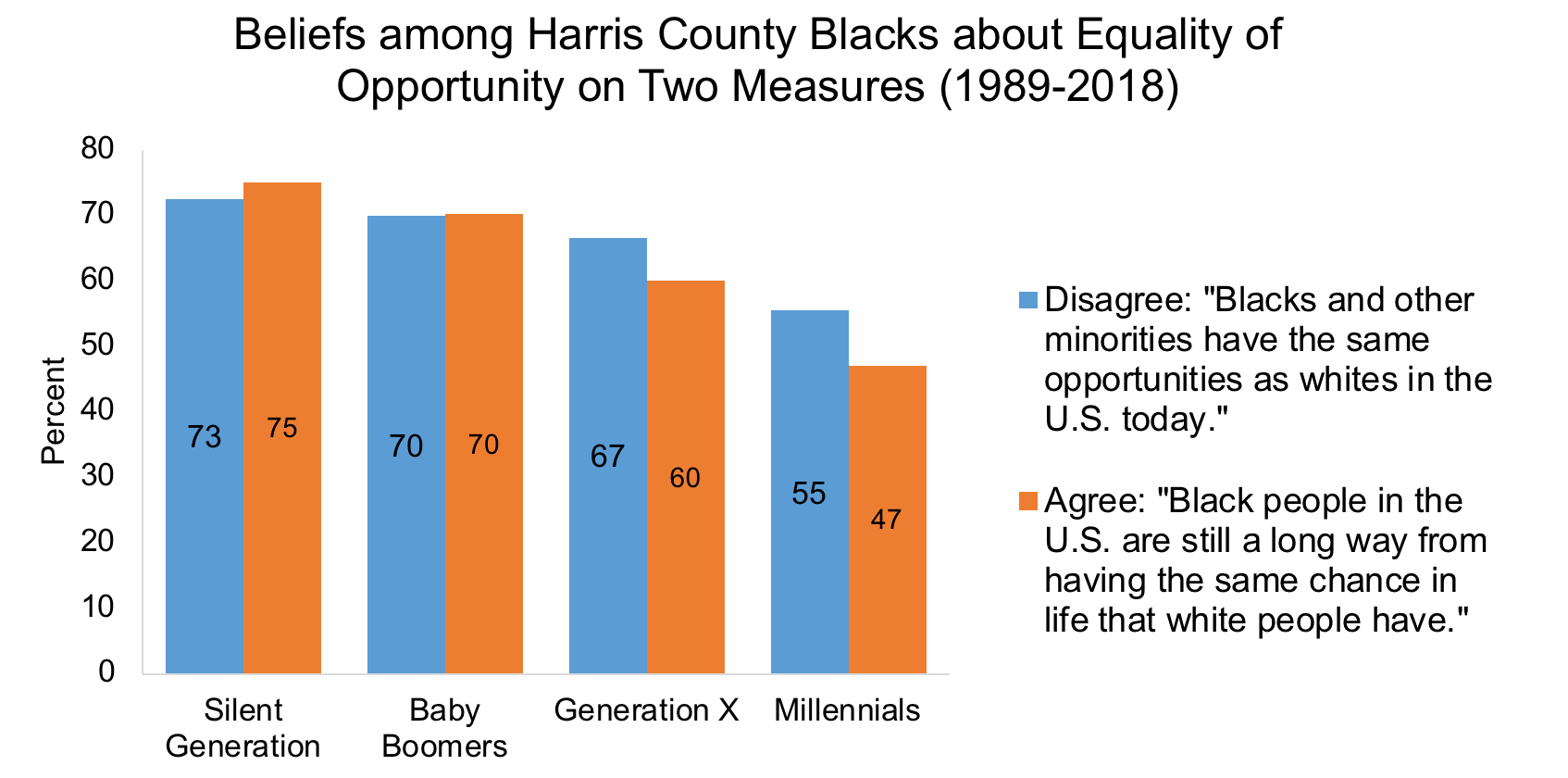
Different generations of African-Americans grew up in worlds with measurably different opportunities, and their experiences may have had a lasting impact on their worldviews. The Silent Generation (born 1928-1945) endured the full effects of the Jim Crow laws. Baby Boomers (1946-1964) were the children of the Civil Rights Movement. Generation X (1965-1980) came of age during the Fair Housing Act and the Black Power Movement. Millennials (1981-2000) benefited greatly from these major successes, despite the continuing realities of racism and discrimination. Are there significant differences between African-American generations in their assessments of black opportunity in America? And if so, in what ways do their perceptions differ?
The findings from the Kinder Houston Area Survey in the years from 1989 to 2018 show that generation is, in fact, a significant predictor of the belief among African-Americans in the extent of equality of opportunity, even after controlling for differences in education, religion, political party, and income. As indicated in the chart, when asked if “blacks and other minorities have the same opportunities as whites in the U.S. today,” fewer Millennials, by a whopping eleven percentage points, disagreed with that assertion, compared to Generation X, the cohort just before theirs, which was next most likely to disagree with that statement. In fact, each of the successive generations exhibited a stronger belief in equality of opportunity than their earlier counterparts.